Isotopes are variants of a specific chemical element. Wsl2 vpn anyconnect. For example, uranium-238, uranium-235 and uranium-234 are three isotopes of the element uranium. The listed numbers are the mass number and each isotope has a different mass number. This number is calculated by adding the amount of protons and neutrons that the isotope contains in the nucleus and it is one of the differences between isotopes from the same element. Let’s find out some of the most common similarities and differences between these isotopes.
Similarities between isotopes of the same element
Each isotope of the same element is identical in most ways including having the same number of protons and electrons.
A new element, Tyserium (Ty), has recently been discovered and consists of two isotopes. One isotope has a mass of 331 g/mol and is 35.0% abundant. The other isotope is 337 g/mole and is 65.0% abundant. What is the mass of Ty as it appears on the periodic table? The isotopes of a chemical element are a group of atoms of that have the same atomic numbers but different mass numbers. This implies that all isotopes of an element have the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei and the same number of electrons in the electron cloud surrounding the nucleus. Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. Isotopes: Any of two or more forms of a chemical element, having the same number of protons in the nucleus, or the same atomic number, but having different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus, or different atomic weights. Isotopes show different physical properties but same chemical properties. Answer verified by Toppr Upvote (0). Isotopes are atoms of an element with the normal number of protons and electrons, but different numbers of neutrons. Isotopes have the same atomic number, but different mass numbers.
Differences between isotopes of the same element
Each isotope of the same element contains a different number of neutrons and this is the main difference between isotopes of the same element. The isotopes will also have a slightly different atomic mass because of the different number of neutrons. Radioactive (unstable) isotopes will also have different half lives (rate of decay). They may also a different type of decay and daughter isotope (daughter product), which is the product left over after radioactive decay.
Did you know?
Many of the elements have at least one stable isotope and a number of unstable (radioactive) isotopes. However, certain elements have no stable isotopes at all. This includes the elements technetium, promethium and every element after lead.
Many radioactive isotopes have very important uses in fields such as geology (radiometric dating), medicine (nuclear medicine), astronomy (radiometric dating), fire prevention (smoke detectors), food preservation (irradiation) and pest control (irradiation).
Related Articles
Isotopes
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that contain different numbers of neutrons. For these species, the number of electrons and protons remain constant. This difference in neutron amount affects the atomic mass (A) but not the atomic number (Z). In a chemical laboratory, isotopes of an element appear and react the same. For this reason, it is difficult to distinguish between an atom's isotopes. In contrast, nuclear scientists can identify and separate different types of atomic nuclei. The technology required for this process is more sophisticated that what could be found in a typical chemical laboratory.
The element carbon ((ce{C})) has an atomic number of 6, which means that all neutral carbon atoms contain 6 protons and 6 electrons. In a typical sample of carbon-containing material, 98.89% of the carbon atoms also contain 6 neutrons, so each has a mass number of 12. An isotope of any element can be uniquely represented as ({}_Z^{A}X) where X is the atomic symbol of the element. The isotope of carbon that has 6 neutrons is therefore (ce{_6^{12}C}) The subscript indicating the atomic number is actually redundant because the atomic symbol already uniquely specifies Z. Consequently, it is more often written as (ce{^{12}C}), which is read as “carbon-12.” Nevertheless, the value of (Z) is commonly included in the notation for nuclear reactions because these reactions involve changes in (Z).
Kinda looks like you've pointed a camera at a screen. But you don't have to bother pointing a camera at your screen. Inspired by the film Catfish. How to Track and Replace a Screen in After Effects. VFX for Motion is packed full of exclusive, in-depth lessons developed by Mark, author of the After Effects Studio Techniques series of books that helped launch a generation of visual effects artists. I had the same black screen issue, tried all sort of different things but it didn't work till I downgraded my after effects 2020 to 2019 and now I have no issues. For my 2020 after effects, the black screen would appear on some projects files and won't appear on some project files. After effects screen. A tutorial on how to view the full screen preview in Adobe After Effects.
Isotopes Of The Same Element Must Have The Same

Most elements on the periodic table have at least two stable isotopes. For example, in addition to (ce{^{12}C}), a typical sample of carbon contains 1.11% (ce{_6^{13}C}), with 7 neutrons and 6 protons, and a trace of (ce{_6^{14}C}), with 8 neutrons and 6 protons. The nucleus of (ce{_6^{14}C}) is not stable, however, but undergoes a slow radioactive decay that is the basis of the carbon-14 dating technique used in archeology. Many elements other than carbon have more than one stable isotope; tin, for example, has 10 isotopes. There are about twenty elements that exist in only one isotopic form (sodium and fluorine are examples of these).
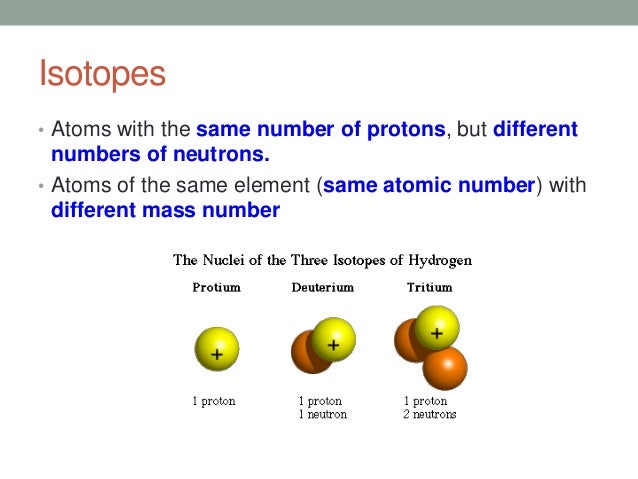
An important series of isotopes is found with hydrogen atoms. Most hydrogen atoms have a nucleus with only a single proton. About 1 in 10,000 hydrogen nuclei, however, also has a neutron; this particular isotope is called deuterium. An extremely rare hydrogen isotope, tritium, has 1 proton and 2 neutrons in its nucleus. Figure (PageIndex{1}) compares the three isotopes of hydrogen.
There are currently over 3,500 isotopes known for all the elements. When scientists discuss individual isotopes, they need an efficient way to specify the number of neutrons in any particular nucleus. Imessage on. A/Z and symbol-mass formats can be used to display periodic table information. When viewing either of these two notations, isotopic differences can be obtained.
The discovery of isotopes required a minor change in Dalton’s atomic theory. Dalton thought that all atoms of the same element were exactly the same.
Isotopes Of The Same Element Have Different
Look at the A/Z formats for the three isotopes of hydrogen in Table (PageIndex{1}). Note how the atomic number (bottom value) remains the same while the atomic masses (top number) are varied. All isotopes of a particular element will vary in neutrons and mass. This variance in mass will be visible in the symbol-mass format of same isotopes as well.
| Common Name | A/Z formats | symbol-mass format | Expanded Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | (mathrm{^{1}_{1}H}) | (text{H-1}) | hydrogen-1 |
| Deuterium | (mathrm{^{2}_{1}H}) | (text{H-2}) | hydrogen-2 |
| Tritium | (mathrm{^{3}_{1}H}) | (text{H-3}) | hydrogen 3 |
Example Of An Isotope
Both A/Z or symbol-mass formats can be utilized to determine the amount of subatomic particles (protons, neutrons, and electrons) contained inside an isotope. When given either format, these mass values should be used to calculate the number of neutrons in the nucleus.
